EARTH IS THE ONLY PLANET in the solar system that is capable of supporting advanced life. Its unique combination of liquid water, a rich oxygen- and nitrogen-based atmosphere, and dynamic weather patterns provide the basic elements for a diverse distribution of plant and animal life. Over millions of years, landforms and oceans have been constantly changing, mountains have been raised up and eroded away,and continental plates have drifted across Earth. The atmosphere acts like a blanket, evening out temperature extremes and keeping warmth in. Without this" greenhouse effect" (p.47), Earth would be about 60°F (33°C) cooler on average. Over the last few decades, scientists have measured a gradual increase in Earth's temperature. Glaciers and polar ice caps have begun to shrink. It is feared that human activity is causing this rapid change by increasing the amount of carbon dioxide and other "greenhouse gases" in the atmosphere. Read some facts about Earth at the bottom, or click here.
Earth and the Moon
The English astronomer James Bradley (1693-1762) noted that many stars appear to have irregularities in their paths. He deduced that this is due to the effect of observing from an Earth that wobbles on its axis, caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon.
Constant Geographical Change
Earth's crust is made up of a number of plates that are constantly moving because of currents that rise and fall from the molten iron core at the center of the planet. Where the plates collide, they can lift the rocky landscape upward to create mountain ranges that are then eroded into craggy shapes like the Andes in Patagonia. The tensions caused by these movements sometimes result in earthquakes and volcanic activity.
Pocket Globe
A globe is a convenient tool for recording specific features of Earth's surface. This 19th-century pocket globe summarizes the face of the world from the geopolitical perspective where the continents are divided into nations and spheres of influence. On the inside of the case is a map of the celestial sphere, with all the constellations marked out.
Early Life on Earth
The first life on Earth was primitive plants that took carbon dioxide from the air and released oxygen during photosynthesis. Animals evolved when there was enough oxygen in the atmosphere to sustain them. Knowledge about evolving life forms comes in the form of fossils in the rocks (left). However, life forms survive only if environmental conditions on Earth are suitable for them. The dinosaurs, for example, though perfectly adapted to their age, became extinct about 65 million years ago.
Fossilized Algae
Dead plants and creatures buried in sediment are slowly turned to rock, becoming fossils. This rock contains the fossilized remains of tiny algae that were one of the earliest life forms.
Human Damage
Many scientists wonder if humans, like the dinosaurs, might also become extinct. The dinosaur seems to have been a passive victim of the changing Earth, while humans are playing a key role in the destruction of their environment. In the year 2000 there were more than 6 billion people on Earth-all producing waste and pollution. In addition to global warming that may be occurring due to the greenhouse effect, chemicals are being released that deplete the ozone layer-a layer in the atmosphere that keeps out dangerous ultraviolet radiation.
Life Giving Atmosphere
Our atmosphere extends out for about 600 miles (1,000 km). It sustains life and protects us from the harmful effects of solar radiation. It has several layers, but the life-sustaining layer is the troposphere, up to 6 miles (10 km) above Earth's surface.
Evolution of the Atmosphere
Since Earth was formed, the chemical makeup of the atmosphere has evolved. Carbon dioxide (C02) decreased significantly between ~,500 and 3,000 million years ago (mya). There was a comparable rise in nitrogen. The levels of oxygen began to rise at the same time, due to photosynthesis of primitive plants, which used up CO2 and released oxygen.
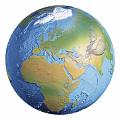
The Spherical Earth
As early as the 5th century BCE the Greek philosophers had proposed that Earth is spherical, and by the 3rd century BCE they had worked out a series of experiments to prove it. But it was not until the first satellites were launched in the late 1950s that humans saw what their planet looks like from space. The one feature that makes Earth unique is the great abundance of liquid water; more than twothirds of the surface is covered with water. Water makes Earth a dynamic place. Erosion, tides, weather patterns, and plentiful forms of life are all tied to the presence of water. There is more water in the Sahara Desert in North Africa than there is on Venus.
Facts About Earth
- Sidereal period 365.26 days
- Temperature -95°F to 130°F (-70°C to 55°C)
- Rotational period 23 hr 56 min
- Mean distance from the Sun 93 million miles! 149.6 million km
- Volume 1 • Mass 1
- Density (water = 1) 5.52
- Equatorial diameter 7,930 miles!12,760 km
- Number of satellites 1 (the Moon)